Forwarded this newsletter and want to see more? Sign up here:
Access archived newsletters here:
Hi, enjoy this weeks curated risk and business updates.
This week we’re going to take a look at Apple’s shift away from their prior endeavors regarding the development of an electric vehicle which they recently scrapped.
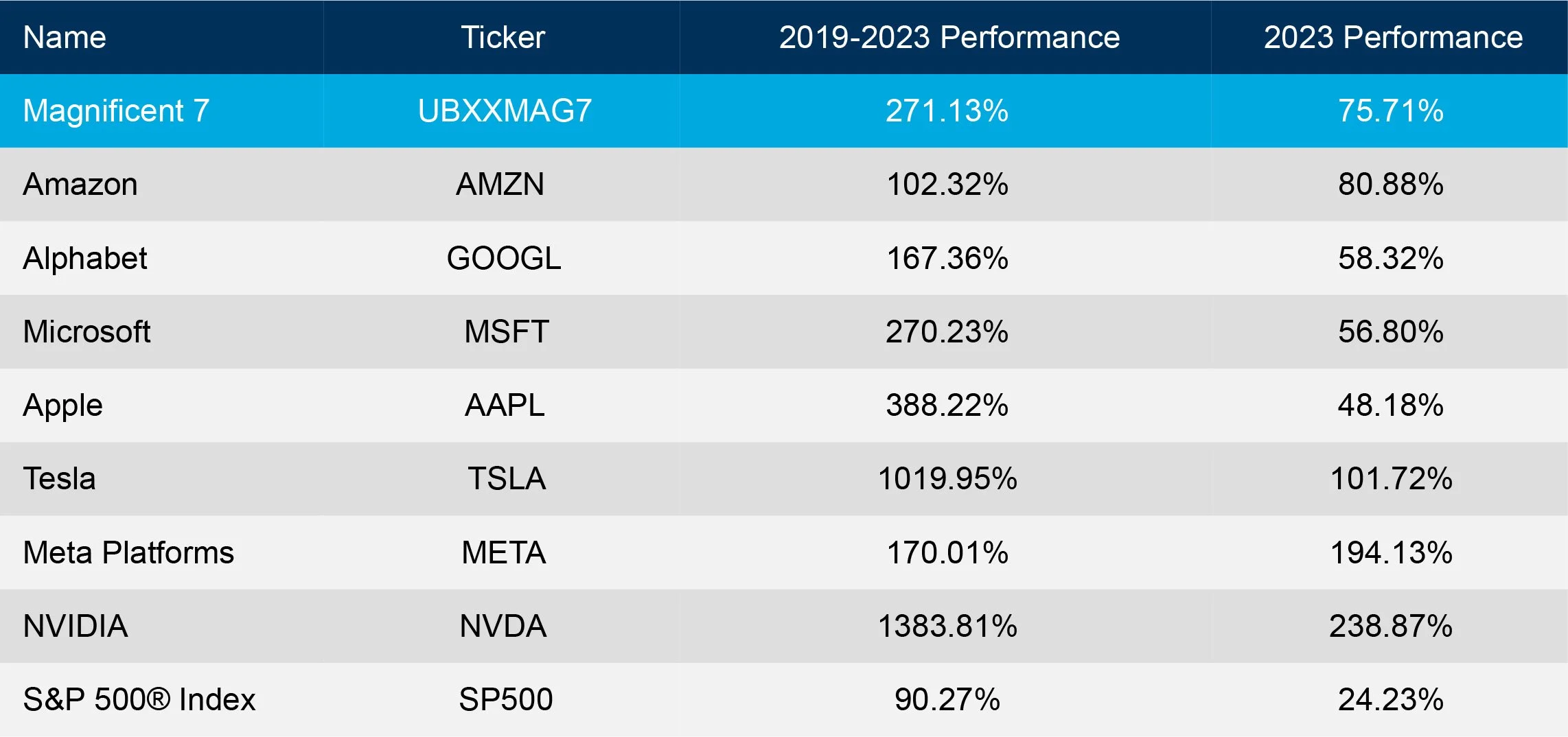
After 10 years of product development challenges and shifting strategies, Apple/s investments in the Apple Car have ceased and its team of up to 2,000 employees have been laid off or redeployed to its generative AI strategy. As other members of the “Magnificent 7” have ridden the AI wave, Apple may have fallen behind and the marketplace has increased questions about its business strategy. Microsoft market capitalization ($3.14Trillion) recently surpassed Apple ($2.72T) and is now the most valuable company in the world
Apple recently pulled the plug on “Project Titan”, its electric vehicle initiative to develop the Apple Car. The Apple Car was meant to be Apple’s next “star product”, with their core competencies around integrating hardware, software and services was going to be a key market differentiator. The Apple Car was intended to be designed around hands off driving, with no steering wheel or pedals. The project saw uneven progress, including a shift in focus to software and a reduction in team size in 2019.
Why would a company with Apple’s resources decide to leave a market opportunity it had invested a decade and significant resources and talent pursuing? Key factors may have included:
Declining Demand for Electric Vehicles due to high interest rates, price, product-market fit and ongoing consumer concerns about battery charging.
Technical and regulatory hurdles made it very challenging to develop and deliver on the Apple Car design and customer experience goals
Automotive industry supply chain and production complexities
Falling behind key competitors such as Microsoft and Google in the generative AI arms race
Although many Project Titan resources have been let go or redeployed to its generative AI efforts, two opportunities for success may yet emerge from Project Titan and related efforts.
CarPlay has fallen behind Android Auto, which is now a fully integrated system, having captured 35% of the auto operating system marketplace, with Polestar, Porsche, BMW, Volkswagen, Ford, Lucid, Stellantis and General Motors all having cars with Android Auto installed. CarPlay has been revamped, and Apple seeks to defend a slice of the Auto market. One key challenge is that CarPlay is still not integrated into the auto operating system like Android Auto.
One potential diamond from the Apple Car investment may be the microprocessor that was intended to be optimized for the intense AI demands of a fully autonomous vehicle and believed to be near complete. It is unclear if the microprocessor has been scrapped or if it will be part of Apple’s generative AI plans going forward.
Apple’s stock price dropped initially following their announcement to cancel Project Titan. However, the marketplace and analysts have turned generally favorable as Apple’s generative AI strategy is beginning to take shape. In addition, Apple is holding talks with generative AI market leaders to determine if the fastest way to catch up is partnering with market leaders like Google or OpenAI. Apple clearly has several key advantages and core competencies in bringing great products to consumers and capturing services revenues from those products.
However, disruptive innovation is real and eventually catches up with all companies.
Ultimately the Disruptors always become the Disrupted.
Request more information on DelCreo’s Risk Universe and risk assessment services.
As a reminder, here are our Risk Universe categories that we leverage to tackle and understand risk which include:
External Risk
Governance Risk
Strategic Risk
Product Risk
Business Operations Risk
Legal & Compliance Risk
Financial Risk
Technology Risk
These high-level risks are fairly consistent between different companies and risk profiles.
We leverage our understanding of risk maps and risk universes to better advise our clients in strategic business decisions and to optimize the management of risk throughout the enterprise.
Weighing the Risks
Weekly Highlights
Intensified Regulation of Generative AI: Governments, including the EU and California, are enforcing new regulations like the Digital Services Act (DSA) to address risks associated with generative AI, such as deepfakes, misinformation, and election integrity.
Proactive Compliance and Advanced Technology Investment: Organizations should stay informed about evolving AI regulations, implement robust risk management strategies, and invest in advanced technologies for cybersecurity and supply chain resilience.
Development of AI Skills and In-House Solutions: Companies should prioritize developing AI skills and consider in-house development of AI solutions for greater efficiency and accuracy in applications like risk detection, fraud prevention, and automation.
Risk Universe Weekly Updates
External Risk
EU dials up scrutiny of major platforms over GenAI risks ahead of elections
The European Commission is requesting information from major tech platforms about their mitigation measures for risks related to generative AI, focusing on issues like deepfakes, misinformation, and election integrity, as part of its enforcement of the Digital Services Act (DSA) rules.
The EU is planning stress tests for these platforms to assess their readiness to handle generative AI risks, particularly in the context of potential political deepfakes ahead of the European Parliament elections, emphasizing the need for platforms to be prepared for incidents that could impact elections.
EU Presses Big Tech Companies on AI Threats
The European Commission is scrutinizing major tech firms' handling of generative AI risks, such as deepfakes and misinformation, under the Digital Services Act (DSA), aiming to ensure compliance with regulations and protect election integrity.
In response to the rise in AI-driven fraud, regulators like the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) are proposing new rules to combat impersonation fraud, emphasizing the need for robust measures and technologies to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
California Forges Ahead With AI Rules as Federal Regulations Lag Behind
California's recent vote highlights growing concerns over AI and personal data use, prompting the state to regulate these technologies in the absence of clear federal laws, setting a potential precedent for national legislation.
The move reflects a broader trend among states, including Washington, New York, and Massachusetts, to control AI, pressuring the federal government to develop a national plan for AI oversight to address specific needs and concerns.
Governance Risk
CEOs are increasingly seen as influential figures in shaping not just their organizations but also broader societal norms and public policy, requiring them to be informed, thoughtful, and proactive in addressing critical issues.
To maximize their impact, CEOs should speak out on issues that impact their organizations and communities, lead with purpose by focusing on initiatives and values that resonate with them personally, and act as catalysts for change by aligning their statements with concrete actions and fostering internal cultures that reflect their commitments.
Product Risk
Microsoft stock hit a record high after launching an AI cybersecurity tool
Microsoft's announcement of its Microsoft Copilot for Security tool, set to launch on April 1, boosted its stock to a record high. The tool is hailed as the AI industry's first generative AI solution for security and IT professionals, trained on large-scale data and threat intelligence.
Despite its AI advancements, some Microsoft employees reportedly believe the company's focus on its partnership with OpenAI has shifted its AI work away from innovation, with concerns that it now primarily serves as tech support for OpenAI rather than driving innovation internally.
Business Operations Risk
Your business could lose money by not updating ancient software. Here’s why
Clunky, old technology in the US costs $2.41 trillion a year in cybersecurity, operational failures, and maintenance, posing significant financial risks to businesses due to potential cybersecurity breaches and operational disruptions.
Business owners, especially those over 50, should consider upgrading their outdated technology to avoid valuation issues when selling their businesses, as buyers may discount purchase prices to cover the costs of upgrading or replacing old systems, highlighting the importance of addressing technology-related risks for long-term business success.
Transforming supply chain resilience with generative AI and data
Companies are increasingly investing in generative AI and other advanced technologies to enhance supply chain management, with a focus on predictive capabilities to forecast and prevent disruptions, optimize planning, and improve decision-making, highlighting the importance of leveraging AI for operational resilience and efficiency.
The adoption of data-driven technologies such as data lakes, control tower layer technology, and digital twins is crucial for companies to achieve end-to-end visibility and collaboration in their supply chains, enabling them to adapt to market changes, enhance flexibility, and drive sustainable growth, emphasizing the significance of modernizing supply chain practices through AI-driven insights and simulations.
Legal & Compliance Risk
Nvidia's lawyer says IP law probably won't apply to AI models
Nvidia's deputy general counsel believes that intellectual property law is unlikely to be extended to cover AI model creations, as it traditionally focuses on protecting human intellectual effort, making it challenging to discern human versus machine contributions in AI-generated content.
Nvidia is facing a lawsuit over allegations of training its AI model on copyrighted work, with authors seeking unspecified damages for unauthorized use of their copyrighted books in building Nvidia's NeMo AI platform.
Financial Risk
VCs will get liquidity in 2024 from the secondary market, not IPOs
Despite expectations from venture capitalists for the IPO market to open up in 2024, there have been no completed major IPOs so far in Q1, with few in progress. Market conditions, including high interest rates and depressed valuations, are making IPOs less appealing to investors, leading them to seek liquidity through secondary markets instead.
Secondary markets are becoming increasingly important, allowing startups to provide liquidity to investors and employees without the need for a premature exit event. These markets offer a way for investors to offload shares, increase stakes in promising startups, and provide cash for employees, reducing the pressure for startups to go public before market conditions are favorable.
Technology Risk
Technology Still Doesn’t Supply The Insights Needed For Supply Chains
Many supply chain executives lack automated systems for observing and predicting disruptions, spending significant time manually tracking data, which poses operational risks and limits their ability to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
Despite the intent to invest in proactive supply chain management, a large percentage of executives still rely on gut decisions due to the absence of predictive data, highlighting the urgent need for technologies such as digital twins and AI to enhance visibility, resilience, and decision-making in supply chain operations.
European Firms' AI Trends Revealed: Cornell Study Highlights Preference for Ready-Made Software
A study by professors at Cornell's Dyson School of Economics and Management analyzed over 3000 European firms using AI, finding that most prefer ready-made AI software that they can customize. This highlights the continued need for people with AI skills to make these technologies effective in firms.
While many industries use off-the-shelf AI software, some are developing their own, with in-house development seen as more efficient and accurate. Industries like science, trade, finance, and real estate are among those adopting AI, primarily for risk detection, fraud prevention, equipment optimization, and automation.